COVID-19 pandemic in Vietnam
This article needs to be updated. |
| COVID-19 pandemic in Vietnam | |
|---|---|
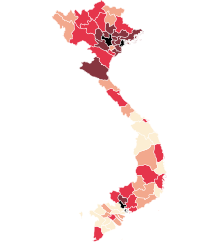 Map of the COVID-19 pandemic in Vietnam: (as of 21 February 2021): Confirmed 10–99
Confirmed 100–999
Confirmed 1.000-9.999
Confirmed 10.000-99.999
Confirmed ≥ 100.000 | |
| Disease | COVID-19 |
| Virus strain | SARS-CoV-2 |
| Location | Vietnam |
| First outbreak | Wuhan, Hubei, China |
| Index case | Ho Chi Minh City |
| Arrival date | 23 January 2020 (4 years, 11 months, 3 weeks and 1 day) |
| Confirmed cases | 2,383[1] |
| Recovered | 1,717[1] |
Deaths | 35[1] |
| Government website | |
| ncov | |
The COVID-19 pandemic spread to Vietnam on 23 January 2020, when its first known case of COVID-19 was reported.[2]
As of 21 February 2021[update] the country had 2,383 confirmed cases, 1,717 recoveries, and 35 deaths. More than 1.7 million tests have been performed.[3] Hai Duong, as of February 2021 is the most-affected province with 647 confirmed cases.[1]
Cases
[change | change source]On 23 January, Vietnam confirmed the first two cases of COVID-19, a Chinese man (#1) travelling from Wuhan to Hanoi to visit his son who lived in Vietnam, and his son (#2), who was believed to have contracted the disease from his father. They were hospitalized in Ho Chi Minh City.[4] On 29 January, the son fully recovered and was discharged.[5] His father was discharged on 12 February.[6]
From 17 to 23 April, no new cases were confirmed.[7][8] However, there were reports of cases who tested positive again after being discharged.[9][10] On 24 April, two more cases were confirmed: both were Vietnamese students who came back from Japan and quarantined on arrival.[11]
Government response
[change | change source]| Stage | Number of case | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Phase 1 (23 January – 25 February 2020) | 16 | Cases reported are usually people who have had travel history to China. |
| Phase 2 (6 – 19 March 2020) | 69 | The virus has spread globally, many cases reported are from other countries but it is still easy to trace spread and quarantine. |
| Phase 3 (20 March – 21 April 2020) | 183 | Infections in community, many cluster begins to appeared in high-density areas. The source of the infection is untraceable. |
| Phase 4 (22 April 2020 – ongoing) | 20 | Even after the consistently decreasing rate of cases from community transmission, health officials remain cautious for importing a second wave through international travelers. |
Praise
[change | change source]Vietnam has been seen by the global media as having one of the best-organised epidemic control programs in the world,[14] along with Taiwan and South Korea.[15]
Despite not having the latest technology, the country's response to the outbreak has received praise for its quick response.[16][17][15][18]
References
[change | change source]- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 "TRANG TIN VỀ DỊCH BỆNH VIÊM ĐƯỜNG HÔ HẤP CẤP COVID-19" (in Vietnamese). BỘ Y TẾ (Ministry of Health). Archived from the original on 2020-02-13. Retrieved 2020-05-14.
- ↑ Coleman, Justine (23 January 2020). "Vietnam reports first coronavirus cases". The Hill. Archived from the original on 18 February 2020. Retrieved 18 February 2020.
- ↑ "Viet Nam COVID-19 Situation Report #29" (PDF). WHO. 9 February 2021. Retrieved 9 February 2021.
- ↑ Phương, Lê (23 January 2020). "Hai người viêm phổi Vũ Hán cách ly tại Bệnh viện Chợ Rẫy" [Two people with Wuhan pneumonia were isolated at Cho Ray Hospital]. VnExpress (in Vietnamese). Archived from the original on 23 January 2020. Retrieved 23 January 2020.
- ↑ Phương, Lê (28 January 2020). "One of Vietnam's first confirmed coronavirus patients recovers". VnExpress. Archived from the original on 29 January 2020. Retrieved 29 January 2020.
- ↑ Phương, Lê (12 January 2020). "Bệnh nhân viêm phổi corona thứ hai ở TP HCM xuất viện" [Second recovered COVID-19 patient in HCMC]. VnExpress (in Vietnamese). Archived from the original on 12 February 2020. Retrieved 12 January 2020.
- ↑ "Chiều nay không ghi nhận thêm ca nhiễm nCoV". Vnexpress. Retrieved April 9, 2020.
- ↑ "Việt Nam liên tục không có ca COVID-19 mới, nhưng người dân không nên chủ quan". Tuổi Trẻ. 19 April 2020. Retrieved April 19, 2020.
- ↑ "'Bệnh nhân 188' tái dương tính sau khi xuất viện". Vnexpress. Retrieved April 19, 2020.
- ↑ "Bệnh nhân Covid-19 thứ 22 tái dương tính lại… âm tính sau khi về Anh". Thanh Niên. 17 April 2020. Retrieved April 19, 2020.
- ↑ "Vietnam cofirmed 270 cases". Dan Tri. Retrieved April 24, 2020.
- ↑ "Toàn cảnh 3 giai đoạn dịch Covid-19 tại Việt Nam" [3 COVID-19 pandemic phases in Vietnam] (in Vietnamese). Retrieved 8 April 2020 – via Thanh Nien.[permanent dead link]
- ↑ "Thủ tướng chỉ thị tiếp tục các biện pháp phòng, chống dịch COVID-19 trong tình hình mới". Vietnam Ministry of Health. Retrieved 25 April 2020.
- ↑ "Financial Times". 24 March 2020. Archived from the original on 24 March 2020. Retrieved 24 March 2020.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 Humphrey, Chris; Pham, Bac (14 April 2020). "Vietnam's response to coronavirus crisis earns praise from WHO". 7News. Retrieved 17 April 2020.
- ↑ Le, Trien Vinh; Nguyen, Huy Quynh (17 April 2020). "How Vietnam Learned From China's Coronavirus Mistakes". The Diplomat. Retrieved 17 April 2020.
- ↑ "[Op-ed] Why Vietnam has been the world's number 1 country in dealing with coronavirus". 4 March 2020.
- ↑ Sullivan, Michael (16 April 2020). "In Vietnam, There Have Been Fewer Than 300 COVID-19 Cases And No Deaths. Here's Why". National Public Radio. Retrieved 17 April 2020.
