Great horned owl
| Great horned owl | |
|---|---|

| |
| Common great horned owl B. v. virginianus | |

| |
| Coastal great horned owl, B. v. saturatus Reifel Migratory Bird Sanctuary, Delta, British Columbia, Canada | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Strigiformes |
| Family: | Strigidae |
| Genus: | Bubo |
| Species: | B. virginianus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Bubo virginianus (Gmelin, 1788)
| |
| Subspecies | |
|
About 12, see text | |
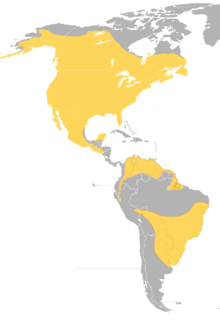
| |
| Global range (all year) of B. virginianus | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Strix virginiana Gmelin, 1788 | |
The Great horned owl (Bubo virginianus) is the largest owl in North America. It is sometimes called the hoot owl.
This widespread bird of prey lives in mountains, grasslands, conifer forests, deserts, chapparals, and many other habitats in North and South America. Its call is a far-carrying hoot.
Description
[change | change source]This owl is 18 to 25 inches (46-64 cm) long and has a wing span of 52 to 55 inches (1.3-1.4 m); its weight averages about 3 pounds (1.5 kg).
The feathers of the horned owl are gray to brown to buff to black. There is a patch of white feathers on the brown chest (called a "gular"). The eyes are yellow with round black pupils.
Diet
[change | change source]The great horned owl hunts and eats mammals (like rabbits, woodchucks, mice, rats, and squirrels), birds (ducks, quail, and geese), and fish.
The owl is at the top of the food web; it has no major predators. It sometimes eats its prey whole and later regurgitates the bones, fur, and feathers in pellets.
References
[change | change source]- ↑ "Bubo virginianus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2014: e.T61752071A61752159. 2014. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2014-2.RLTS.T61752071A61752159.en.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|authors=ignored (help)

