Haloarchaea
Appearance
| Archaea Temporal range: Archaean – Recent
| |
|---|---|
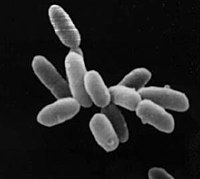
| |
| Halobacteria sp. strain NRC-1, each cell about 5 μm long. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
Haloarchaea are halophiles. They need high salt concentrations to grow. They are a distinct evolutionary branch of the Archaea, and are extremophiles.
The term halobacteria is a misnomer (mistaken name), because we now know the archaea are a different group from bacteria.

In taxonomy, the Haloarchaea are a class of the Euryarchaeota,[1] found in water with salt. They are common in most environments where large amounts of salt, moisture, and organic material are available.
References
[change | change source]- ↑ See the National Center for Biotechnology Information webpage on Halobacteria. Data extracted from the "NCBI taxonomy resources". NCBI. Retrieved 2007-03-19.
