Hemoglobin
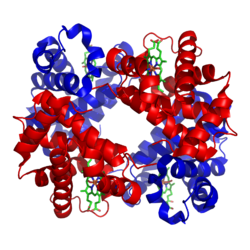
The α and β subunits are in red and blue.
The iron-containing heme groups in green
Hemoglobin (or haemoglobin) is a protein in red blood cells which contains iron. It is used to transport oxygen around the human body.[1]
Hemoglobin is found in the red blood cells of almost all vertebrates. The exceptions are the fish family Channichthyidae,[2] and the tissues of some invertebrates.[3] It does occur in some invertebrates, but most invertebrates use other chemicals, such as hemocyanin.
Hemoglobin is involved in the transport of other gases. It carries some of the body's respiratory carbon dioxide (about 20-25% of the total).[4]
Red blood cells get their colour from hemoglobin, which is red. There are millions of hemoglobin molecules in each red blood cell and millions of red blood cells in the human body. When hemoglobin has oxygen attached, it is called oxyhemoglobin.
Structure
[change | change source]The most common type of hemoglobin in mammals contains four such subunits. Each subunit of hemoglobin is a globular protein (globin) with a heme group inside it. Each heme group has one iron atom. This binds one oxygen molecule. So the complete hemoglobin molecule has four globin chains, four heme molecules, and four iron atoms.[5] When hemoglobin is in the lungs, it picks up oxygen in its hemes, and carries it to the rest of the body.
Its structure took years to work out. Max Perutz and John Kendrew worked out the structure of myoglobin first. That muscle globin is smaller, with only one heme group.
References
[change | change source]- ↑ "Hemoglobin Overview". sickle.bwh.harvard.edu.
- ↑ Sidell, Bruce; Kristin O'Brien (2006). "When bad things happen to good fish: the loss of hemoglobin and myoglobin expression in Antarctic icefishes". The Journal of Experimental Biology. 209 (Pt 10): 1791–802. doi:10.1242/jeb.02091. PMID 16651546.
- ↑ "What is Hemoglobin? (with pictures)". wiseGEEK.
- ↑ Patton, Kevin T. (2015-02-10). Anatomy and Physiology. Elsevier Health Sciences. ISBN 9780323316873.
- ↑ Hemoglobin synthesis
