MERS
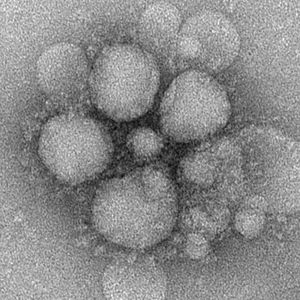
MERS (the Middle East Respiratory Syndrome) was discovered in Saudi Arabia in 2012. It is a disease caused by a coronavirus whose label is MERS-CoV. MERS-CoV is a betacoronavirus which originated in bats.
Coronaviruses are a family of viruses some of which cause common colds. They can infect both animals and people. MERS is a relative of SARS (the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome) virus which swept around the world, infecting more than 8,000 people globally and killing 774 before it was stopped in 2004.
In 2015, the World Health Organization made itself some rules for naming viruses: No official name is allowed to refer to a place, person or animal. This is to prevent stigma, or blame. The WHO rules list MERS as an example of what not to do when naming a virus or disease.[1][2]
References
[change | change source]- ↑ Sanya Mansoor (February 11, 2020). "What's in a Name? Why WHO's Formal Name for the New Coronavirus Disease Matters". Time. Retrieved February 13, 2020.
- ↑ Brett Dahlberg and Elena Renken (February 11, 2020). "New Coronavirus Disease Officially Named COVID-19 By The World Health Organization". NPR. Retrieved February 12, 2020.
