Overseas France


Overseas France (French: France d'outre-mer) is the part of France that is outside of the European continent. It consists of all overseas departments, territories and collectivities. These territories have several different legal statuses and levels of autonomy. Overseas France includes island territories in the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian oceans, French Guiana in South America, and Adélie Land in Antarctica. Each inhabited territory is represented in both the French National Assembly and the French Senate (which together make up the Parliament of France).
2,685,705 people lived in the overseas departments and territories in January 2011.[1]
Types of territories
[change | change source]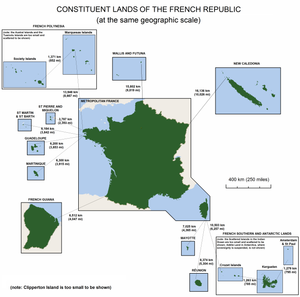
Overseas departments and regions
[change | change source]Overseas departments and regions are completely part of France.
- Guadeloupe (since 1946)
- Martinique (since 1946)
- French Guiana (since 1946)
- Réunion (since 1946)
- Mayotte (since 2011)
- From 1976 to 2003, Mayotte was a unique overseas territory. Between 2003 and 2011, it was an overseas community. It became an overseas department on 31 March 2011, after its citizens voted to become a full part of France.
Overseas collectivities
[change | change source]The category of overseas collectivity was created by changes made to France's constitution in 28 March 2003. Each overseas collectivity has its own written laws.
- French Polynesia (since 2003)
- From 1946 to 2003, French Polynesia was an overseas territory. In 2004, it was given the designation of overseas country (French: pays d'outre-mer).
- Saint Pierre and Miquelon (since 2003)
- From 1976 to 1985, Saint Pierre and Miquelon was an overseas department. Between 1985 and 2003, it was a unique overseas territory.
- Wallis and Futuna (since 2003)
- From 1961 to 2003, Wallis and Futuna was an overseas territory.
- Saint Martin and Saint Barthélemy (since 2007)
- Saint Martin and Saint Barthélemy both separated from Guadeloupe in 2003.[2] They became separate overseas collectivities of their own on 22 February 2007.[3][4]
Special collectivity
[change | change source]- New Caledonia (since 1999)
- New Caledonia was classified as an overseas territory from 1946. It gained a special status in 1999 as a result of the Nouméa Accord. It has its own citizenship, and power is gradually being passed from the French state to New Caledonia itself. A referendum on independence is to be called any time between 2014 and 2019.[5]
Overseas territories
[change | change source]- French Southern and Antarctic Lands (since 1956)
Minor territories
[change | change source]- Clipperton Island is held as private property under the direct authority of the French government. It has no permanent population.
Representation
[change | change source]The overseas departments and territories are represented by 27 députés in the French National Assembly and 21 senators in the French Senate. This is 4.7% of the 577 députés and 6% of the 343 senators.
- Réunion: 7 députés and 4 senators
- Guadeloupe: 4 députés and 3 senators
- Martinique: 4 députés and 2 senators
- French Polynesia: 3 députés and 2 senators
- French Guiana: 2 députés and 2 senators
- Mayotte: 2 député and 2 senators
- New Caledonia: 2 députés and 2 senators
- Saint Pierre and Miquelon: 1 député and 1 senator
- Wallis and Futuna: 1 député and 1 senator
- Saint Barthélemy and Saint Martin: 1 député and 2 senators
List of territories
[change | change source]Inhabited departments and collectivities
[change | change source]The 11 French Overseas Territories are :
| Flag | Name | Capital | Population | Land area (km2) | Status | Location | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| French Guiana | Cayenne | 229,000 (Jan. 2009)[6] | 83,534 | Overseas department / region | South America | ||
| French Polynesia | Papeete | 264,000 (Jan. 2009)[7] | 4,167 | Overseas collectivity | South Pacific Ocean | ||
| Guadeloupe | Basse-Terre | 404,000 (Jan. 2009)[6] | 1,628 | Overseas department / region | Antilles | ||
| Martinique | Fort-de-France | 402,000 (Jan. 2009)[6] | 1,128 | Overseas department / region | Antilles | ||
| Mayotte | Mamoudzou | 186,452 (July 2007)[8] | 374 | Overseas department / region | Africa (Mozambique Channel) |
Also claimed by Comoros | |
| New Caledonia | Nouméa | 244,410 (Jan. 2008)[9] | 18,575 | Sui generis collectivity | South Pacific Ocean | Referendum for independence to occur sometime during the period of 2014 to 2019. | |
| Réunion | Saint-Denis | 817,000 (Jan. 2009)[6] | 2,512 | Overseas department / region | Africa (Indian Ocean) |
||
| Saint Barthélemy | Gustavia | 8,450 (Jan. 2007)[10] | 21 | Overseas collectivity | Antilles | Detached from Guadeloupe on 22 February 2007. | |
| Saint Martin | Marigot | 35,925 (Jan. 2007)[10] | 53 | Overseas collectivity | Antilles | Detached from Guadeloupe on 22 February 2007. | |
| Saint Pierre and Miquelon | Saint-Pierre | 6,099 (Jan. 2007)[10] | 242 | Overseas collectivity | Southeast of Canada | ||
| Wallis and Futuna | Mata-Utu | 13,484 (Jul. 2008)[11] | 274 | Overseas collectivity | South Pacific Ocean |
| Overall Summary | ||
|---|---|---|
| Status | Population (Jan. 2011)[1] | Land area (km2) |
| Overseas Departments / Regions | 1,890,705 | 91,847 |
| Overseas Collectivities & New Caledonia | 795,000 | 23,632 |
| Total | 2,685,705 | 120,049 |
Uninhabited lands
[change | change source]Lands generally uninhabited, except by researchers in scientific stations.
| Flag | Name | Capital | Land area (km2) | Status | Location | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Banc du Geyser | - | 1 | TAAF district | Africa (Mozambique Channel) |
Claimed by Madagascar and Comoros | |
| Bassas da India | - | 1 | TAAF district | Africa (Mozambique Channel) |
Claimed by Madagascar | |
| Clipperton | - | 7 | French state private property | West of Mexico | ||
| Crozet Islands | Alfred Faure | 352 | TAAF district | South Indian Ocean | ||
| Europa | - | 28 | TAAF district | Africa (Mozambique Channel) |
Claimed by Madagascar | |
| Glorioso Islands | - | 5 | TAAF district | Indian Ocean | Claimed by Comoros, Madagascar and Seychelles | |
| Juan de Nova | - | 5 | TAAF district | Africa (Mozambique Channel) |
Claimed by Madagascar | |
| Kerguelen Islands | Port-aux-Français | 7,215 | TAAF district | South Indian Ocean | ||
| Saint-Paul Island and Amsterdam Island |
Martin-de-Viviès | 66 | TAAF district | Indian Ocean | ||
| Tromelin Island | - | 1 | TAAF district | Indian Ocean | Claimed by Mauritius |
Antarctica
[change | change source]| Flag | Name | Capital | Land area (km2) | Status | Location | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adélie Land | Dumont d'Urville Station | 432,000 | TAAF district | Antarctica | Under terms of Antarctic Treaty System |
Related pages
[change | change source]- French colonial empire
- Government of France
- Communes in France
- Metropolitan France
- Organisation internationale de la Francophonie
References
[change | change source]- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Bilan démographique 2010". INSEE. Retrieved 2011-01-21. (in French)
- ↑ "French Caribbean voters reject change". Caribbean Net News. 2003-12-09. Retrieved 2007-02-09.
However, voters in the two tiny French dependencies of Saint-Barthélemy and Saint-Martin, which have been administratively attached to Guadeloupe, approved the referendum and are set to acquire the new status of "overseas collectivity".
- ↑ Magras, Bruno (2007-02-16). "Letter of Information from the Mayor to the residents and non-residents, to the French and to the foreigners, of Saint Barthelemy" (PDF). St. Barth Weekly. p. 2. Retrieved 2007-02-18.
On February 7 of this year, the French Parliament adopted the law granting Saint-Barthélemy the Statute of an Overseas Collectivity.
- ↑ "Saint-Barth To Become An Overseas Collectivity" (PDF). St. Barth Weekly. 2007-02-09. p. 2. Retrieved 2007-02-09.
- ↑ "Nouvelle-Calédonie", Le Petit Larousse (2010), Paris, page 1559.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 "Population des régions au 1er janvier". INSEE. Retrieved 2010-01-30. (in French)
- ↑ Institut Statistique de Polynésie Française (ISPF). "Enquêtes & Répertoires > État Civil". Archived from the original on 2012-01-18. Retrieved 2009-09-14.
- ↑ (in French) "INSEE Infos No 32" (PDF). INSEE. Retrieved 2007-12-02.
- ↑ (in French) Institut de la statistique et des études économiques de Nouvelle-Calédonie (ISEE). "CHIFFRES CLÉS - Démographie". Archived from the original (PDF) on 2008-12-22. Retrieved 2009-01-13.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 "Populations légales 2007 pour les départements et les collectivités d'outre-mer". INSEE. Retrieved 2010-01-30. (in French)
- ↑ "Les populations des circonscriptions du Territoire des îles Wallis et Futuna". INSEE. Retrieved 2009-01-13. (in French)
Other websites
[change | change source]- Official website Archived 2005-10-12 at the Wayback Machine
