State of Franklin
Appearance
| The State of Franklin (Frankland) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||
| August 1784 – December 1788 | |||||||||
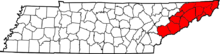 The state of Franklin highlighted on a map of Tennessee | |||||||||
| Capital | Provisional Jonesborough, August 1784 – December 1785 | ||||||||
| Area | |||||||||
| • Coordinates | 36°10′N 82°49′W / 36.167°N 82.817°W | ||||||||
| History | |||||||||
| Government | |||||||||
| • Type | Republic / Organized, extralegal territory | ||||||||
| "Governor" (President) | |||||||||
• December 1784 – December 1788 | President/Governor Col. John Sevier | ||||||||
| Speaker of the Senate | |||||||||
• December 1784 – December 1788 | Landon Carter | ||||||||
• Speaker of the House August 1784 – June 1785 | William Cage | ||||||||
• Speaker of the House June 1785 – December 1788 | Col. Joseph Hardin | ||||||||
| Legislature | Congress of Greeneville | ||||||||
• Upper house | Senate | ||||||||
• Lower House | House of Representatives | ||||||||
| Historical era | post American Revolution | ||||||||
• North Carolina cedes the Washington District to federal government | April 1784 | ||||||||
• Secedes from North Carolina and blocks federal government claims; Franklin proclaimed | August 23 1784 | ||||||||
• Petition for Frankland statehood sent to Congress | May 16, 1785 | ||||||||
• Provisional name changed to "Franklin" | December 24, 1785 | ||||||||
• Disbanded; and re-acquired by North Carolina | March–September 1788 1788 | ||||||||
• Area is designated part of the Southwest Territory | 1790 | ||||||||
| Political subdivisions | Counties | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Today part of | East Tennessee, United States | ||||||||
The State of Franklin (also the Free Republic of Franklin or the State of Frankland) was a part of the United States of America that wanted to become a U.S. state. The proposed state was located in what is now the eastern part of Tennessee.[1]
